How to Comply with OOOOb - Tank Low Pressure Flare Requirements example
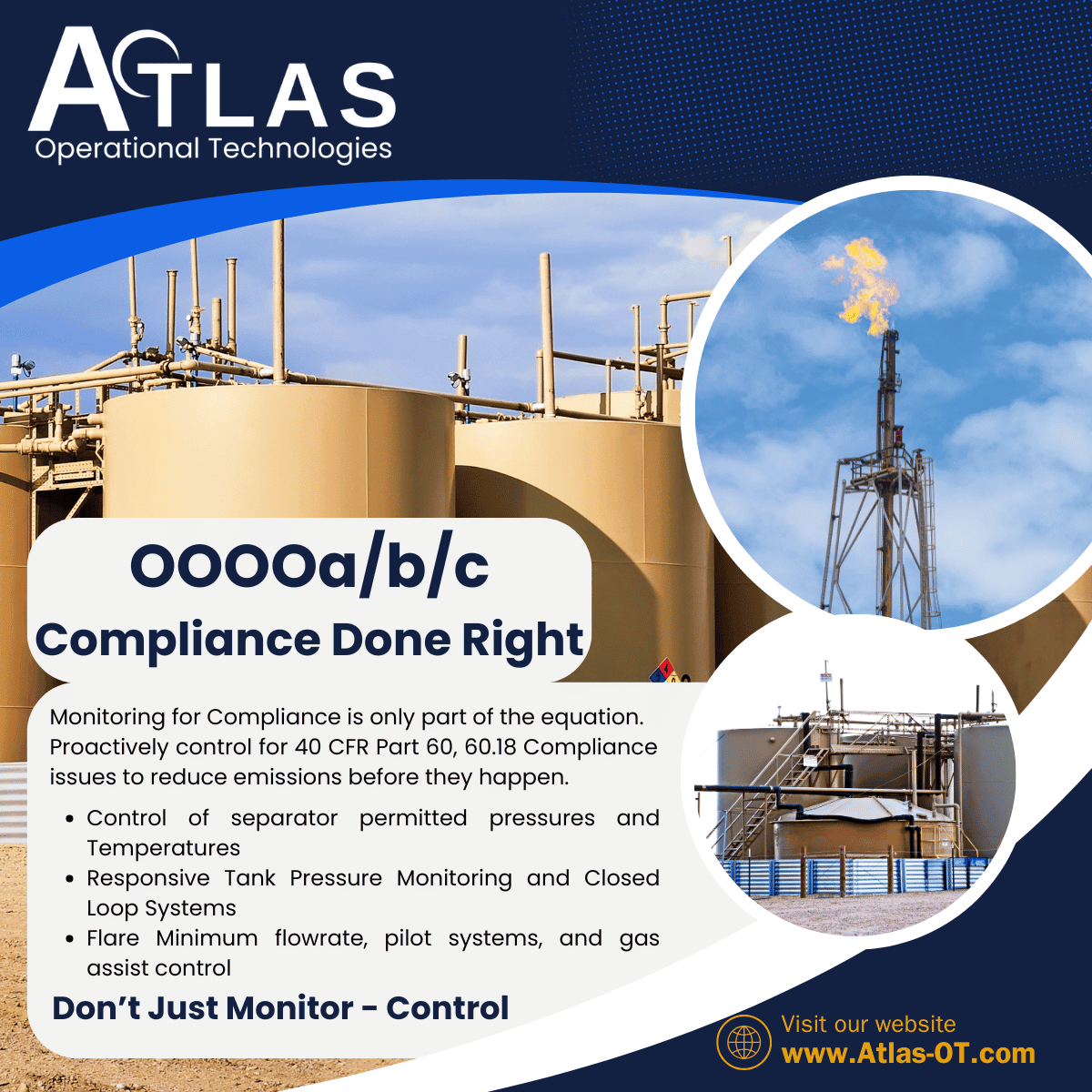
What are Tank Low Pressure Flare Requirements and how does that impact your compliance with OOOOa/b/c? In short, the key is to make sure your flares are always burning efficiently to meet VOC destruction requirements.
Atlas OT can help you with meeting regulatory compliance by meeting Net Heating Value requirements of 60.18 by confirming the air / gas mixture is correct and that you are flowing the correct amount of gas to the flare, confirming flare pilot status is on and validated with an OGI camera.
Flare Curves
Review your pressure vs flare curves from flare vendor. Ensure control system operates in ideal zone for VOC destruction and alert if out of bands.
Gas Composition
Working with The Valor Method, we can determine gas composition (sample and simulation) to find Minimum and Maximum Allowable Flare Flowrate
Inlet Valving
Control system and automation logic to ensure flare inlet valves operate flare within acceptable ranges.
Tank Pressure Monitoring
Solve NHV issues with Tank Pressure Data Monitoring and Control to keep positive pressure on tanks, to prove closed system seal and prevent oxygen egress and thief hatch leaking.
Blower Ramping
Control blowers based on flare inlet pressure, tank pressure, and separator pressure to proactively manage system fluctuations.
Pilot Status
Confirm Flare Pilot Status with direct monitoring and thermocouple data. Track pilot time under temperature to monitor for reportable events.
Overview of 40 CFR 60 Subpart OOOOa OOOOb OOOOc
Overview of 40 CFR 60 Subpart OOOOa OOOOb OOOOc
- Regulates volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from specific sources in the oil and natural gas industry
- Covers emissions from leaking components at onshore natural gas processing plants
- Provides standards for sulfur dioxide emissions from natural gas processing plants
- Gas Well Completions
- Centrifugal and Reciprocating Compressors
- Pneumatic Controllers
- Storage Vessels
- Equipment Leaks at Natural Gas Processing Plants
- Sweetening Units at Natural Gas Processing Plants
Impact of Industrial Automation and Controls
Industrial control systems such as RTUs (Remote Terminal Units), Flow Computers, PLCs (Programming Logic Controllers), and SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition Systems) can significantly enhance compliance efforts while optimizing operations. In many case, compliance can also lead to increased profits on the facility by modernizing control systems for better operations and maintenance.
1. Continuous Monitoring and Data Collection
- Early detection of leaks or equipment malfunctions
- Automated alerts for potential compliance issues
- Improved accuracy in emissions reporting
2. Automated Control Systems
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Distributed Control Systems (DCS) can automate processes to maintain optimal operating conditions:- Precise control of pneumatic controllers to minimize emissions
- Automated adjustment of compressor operations to reduce fugitive emissions
- Optimized storage vessel pressure management
3. Advanced Analytics and Reporting
Data analytics platforms and visualization tools can process the collected data to:- Generate automated compliance reports
- Identify trends and potential areas for improvement
- Support data-driven decision-making for EHS initiatives
4. Remote Monitoring and Control
SCADA systems and remote access technologies allow for:- Real-time monitoring of multiple facilities from a central location
- Rapid response to potential compliance issues
- Reduced need for on-site personnel, improving safety
5. Predictive Maintenance
Machine learning algorithms can analyze equipment performance data to:- Predict potential failures before they occur
- Schedule maintenance proactively to prevent emissions-related issues
- Optimize equipment efficiency and lifespan
Benefits of Automation for Compliance
- Improved Accuracy: Automated systems reduce human error in data collection and reporting.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined processes and optimized operations lead to reduced emissions and improved resource utilization.
- Cost Savings: Proactive maintenance and optimized operations can lower overall compliance costs.
- Simplified Reporting: Automated data collection and report generation save time and resources.
- Increased Safety: Remote monitoring and automated controls reduce the need for personnel in potentially hazardous areas.